Some common error status codes are mention below.
| Code | Description | Comments |
| 0 | It indicates successful execution. | |
| 1 | It is used to catch all general errors. | “Divide by zero”, “Operation not permitted” etc. can be the error messages of this code. |
| 2 | It indicates the abuse of shell built-ins. | “Missing keyword”, “No such file or directory” etc. can be the error messages of this code. |
| 126 | It generates when the any command is unable to execute. | Permission problem or required key not available can generate this status code |
| 127 | It normally generates for the command path problem. | “Command not found” can be the message for this error code. |
| 130 | It generates for fatal error. | “Script terminated by Ctrl+C” can be the message of this code. |
| 255* | It indicates exit code out of range. |
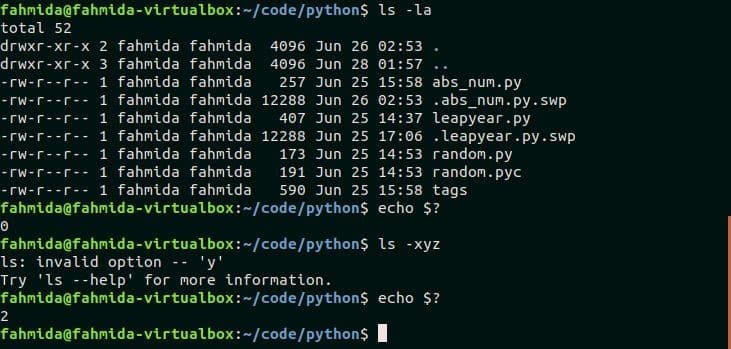
Example-1: Reading exit code from the terminal
‘$?’ shell variable can be used to display the exit code of any command. ‘ls –la’ is a valid command and it shows the list of files and folders of the current working directory. The value of ‘$?’ will be 0 after executing ‘ls -la’ command. ‘ls –xyz’ is an invalid command and ‘$?’ will return 2 as error code after executing the command.
$ echo $?
$ ls -xyz
$ echo $?
Example-2: Reading exit code in bash script
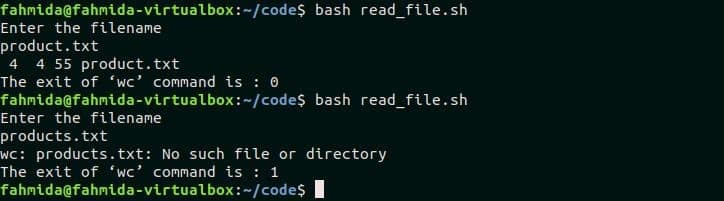
Create a bash file named read_file.sh with the following script. In this script, the file name will be taken as user’s input and, total number of lines, words and characters of that file will be counted by using `wc` command. If the file name is valid then the value of $status_code is 0 and if the file name is invalid, then then the value of $status_code is 1.
read_file.sh
echo "Enter the filename"
read filename
wc -lwc $filename
status_code=$?
echo "The exit of ‘wc’ command is : $status_code"
Example-3: Using exit code value for doing specific task
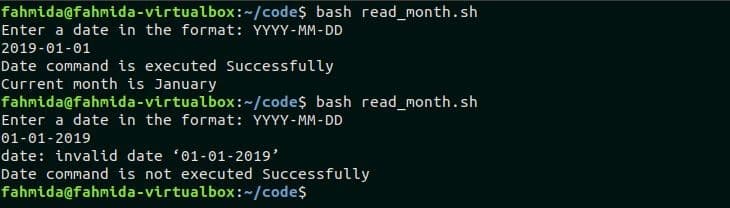
Create a bash file named read_month.sh with the following code. Here, a date value will be taken as input. The name of the month will retrieve from the date value if the input date is valid otherwise “invalid date” error message will appear. ‘if’ condition is used in the script to check the exit status code of the date command. If the condition is true, then the success message and month name of the date will be printed. If the condition is false, then the failure message and exit status code, 1 will print.
read_month.sh
echo "Enter a date in the format: YYYY-MM-DD"
read date_value
current_month=$(date -d "$date_value" ‘+%B’)
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Date command is executed Successfully"
echo "Current month is $current_month"
else
echo "Date command is not executed Successfully"
exit 1
fi
Run the script.
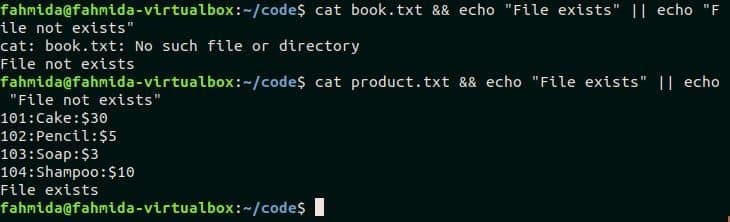
Example-4: Using && and || with exit code
‘&&’ Logical operator is used for successful exit code and ‘||’ logical operator is used for unsuccessful exit code. The following command will print ‘File exists’ if book.txt file exists in the current location and print ‘File not exists’ if book.txt file not exists in the current location.
Conclusion:
Different uses of exit status code are shown in this tutorial. Hope, the reader will get a clear concept about exit status code of bash after reading this tutorial.







