Although, it is a time-consuming task, but once you know how to mount USB drive in LINUX, you will feel lightened and it would be easier for you to perform it the next time when needed. If you are having an updated LINUX System, and a modern computer environment, then your device shall show up on the desktop of your PC itself, but to make it happen at even an older computer, you need to read this article.
Here, in this article, we will discuss about how to mount USB drive in LINUX along with instructions on how to create, delete & format a USB Drive straight from your LINUX system. This should be an easy task once you get the hang of it, just make sure you follow all the steps carefully and you won’t have problems the next time you decide to mount your USB drive in Linux.
1) Plug-in your USB drive to your PC
First, you need to plug in your USB drive to your LINUX-based personal computer (PC) in which you want to access the USB drive.
2) Detecting the USB Drive on PC
The second step is the most important and easy step to accomplish. After plugging-in your USB device to your LINUX system’s USB port, the system will add a new block device into the /dev/ directory. To check that, use the following command – Firstly, open your command line and write the following command in CLI:
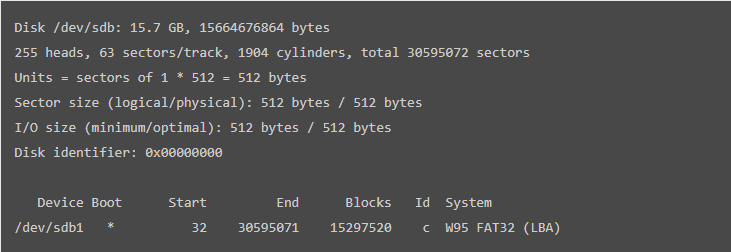
The resulting screen should be seen with the text like this:
The result above shows that device boot, blocks, id and system format are displayed.
After this step, you will need to create a mount point. In order to do so,
3) Create a Mount Point
In this step, we will guide you to create the mount point. Just type the following command to move forward:
In above given command, ‘sbd1’ refers to the name of your USB Device.
4) Creating a Directory in the USB Drive
Next, you will be required to create a directory in the mounted device. For that, use the following command:
/mnt$ mkdir John
Above commands will create a directory named ‘John’ in the USB Drive. You can create the directory of your desired name by replacing it with John. e.g.
/mnt$ mkdir Google
This command will create a directory in the USB Drive with the name ‘Google’.
This step will complete your query of how to mount USB Drive in LINUX. After this step, a new directory will be created
5) Delete a Directory in USB Drive
After telling you about creating a Directory on your USB, its time to learn about how you can delete a directory on your USB Drive. To delete a directory, write the following command:
The above given command will delete the drive named as ‘John’. But if you want to delete a directory with your desired name, just replace it with ‘John’. e.g.
The above code deletes the directory named ‘Google’. Similarly, you can write any of your desired name to delete a directory on your USB Drive on a LINUX operated computer.
6) Formatting the Mounted USB in LINUX
In order to format a USB Flash Drive, you need to unmount the drive first. Use following command to un-mount the USB:
In above-given command, ‘sbd1’ refers to the name of your USB Device. Next, you have to choose either of the following codes as per your USB Drive file systems:
- For VFAT (FAT32) File System
To format VFAT (FAT32) file system, use:$ sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1In above given command, ‘sbd1’ refers to the name of your USB Device.
- For NTFS File System
To format NTFS file system USB Drive, use:$ sudo mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdb1In above given command, ‘sbd1’ refers to the name of your USB Device.
- For EXT4 File System
For formatting EXT4 file system USB Drive, use:$ sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1In above given command, ‘sbd1’ refers to the name of your USB Device.
With that I have showed you the basics of mounting UBS drives on linux.