In this article, I will show you how to add a package repository on Debian. I will use Debian 9 Stretch for the demonstration.
Adding a Package Repository Manually on Debian
The package repository information is stored on the /etc/apt/sources.list file. You may edit the /etc/apt/sources.list file directly to add a new package repository.
You can run the following command to edit /etc/apt/sources.list file:
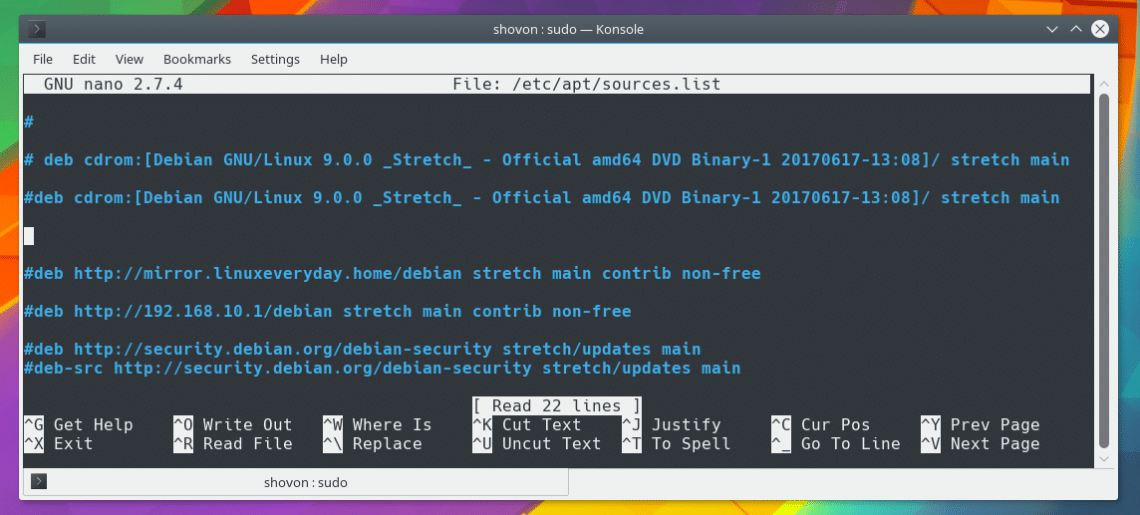
You should see the following window as shown in the screenshot below. As you can see, I have no package repository added here right now. You may have many package repositories added. But I want to show you the basics.
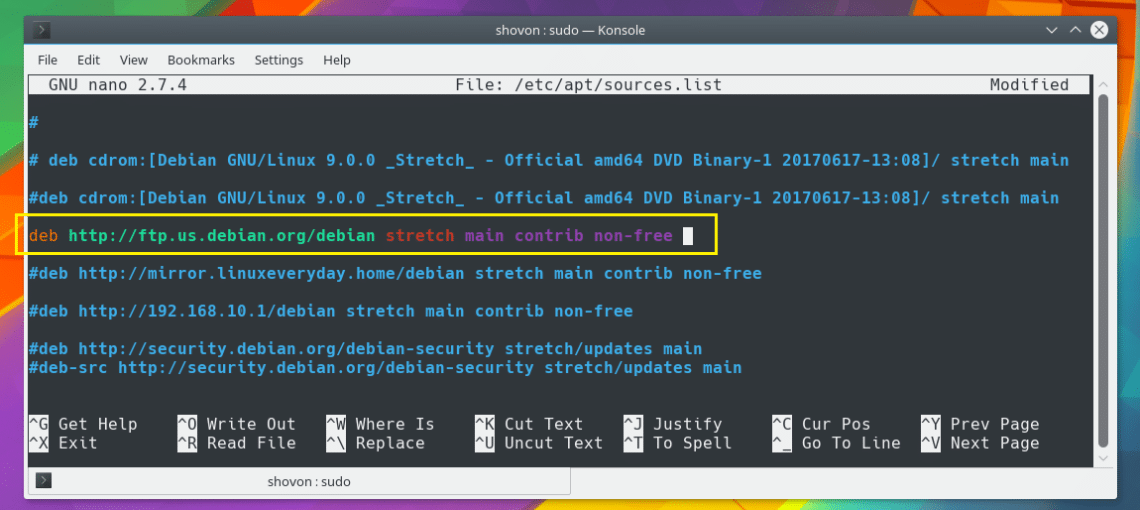
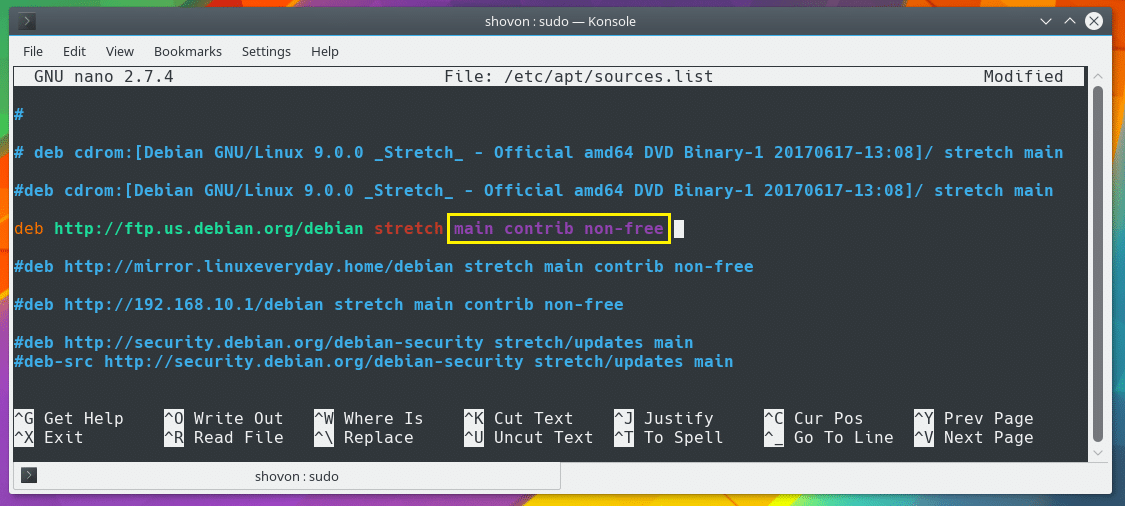
Now I am going to add the official Debian 9 package repository. So I am adding the following line to the file as marked in the screenshot below:
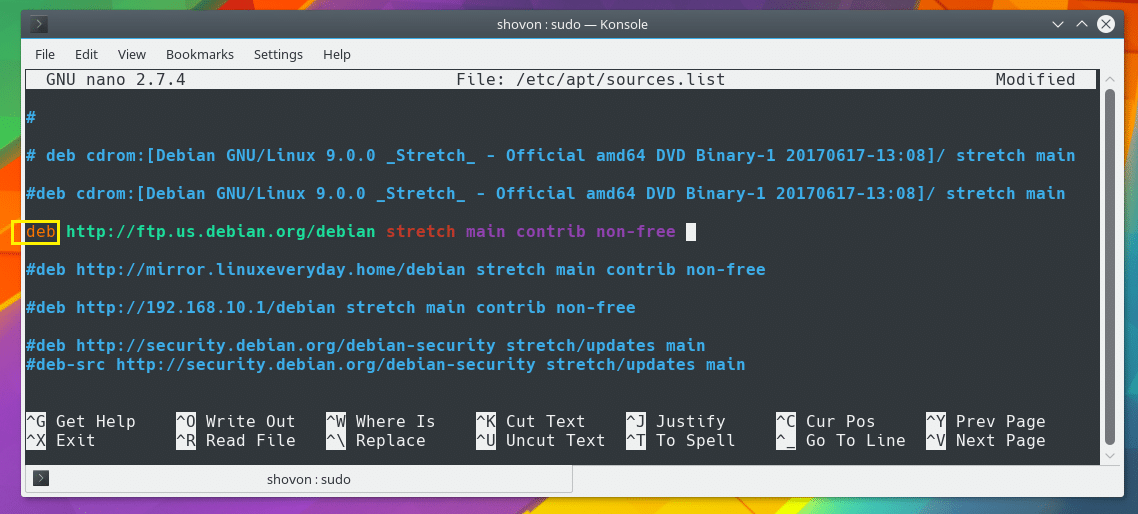
You may not understand what this line is yet. Let me explain.
The line starts with deb which means it’s a pre-compiled Debian binary repository. If the package repository contains source codes of different softwares, you should replace deb with deb-src.
Now the next section is the URL of the package repository. You can add HTTP, HTTPS, FTP repository URLs here.
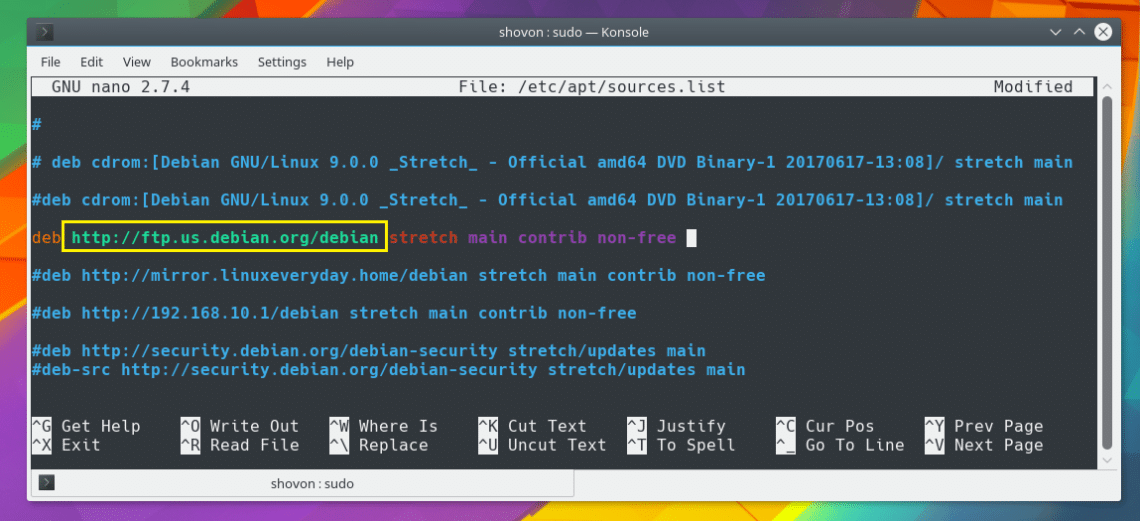
The next section as marked in the screenshot below is the suite or codename. For Debian 9, it is stretch.
You may be able to find what it is for your Debian operating system with the following command:
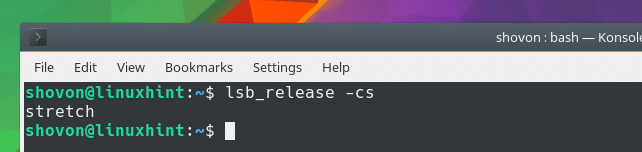
As you can see from the screenshot below, the codename or suite name is stretch.
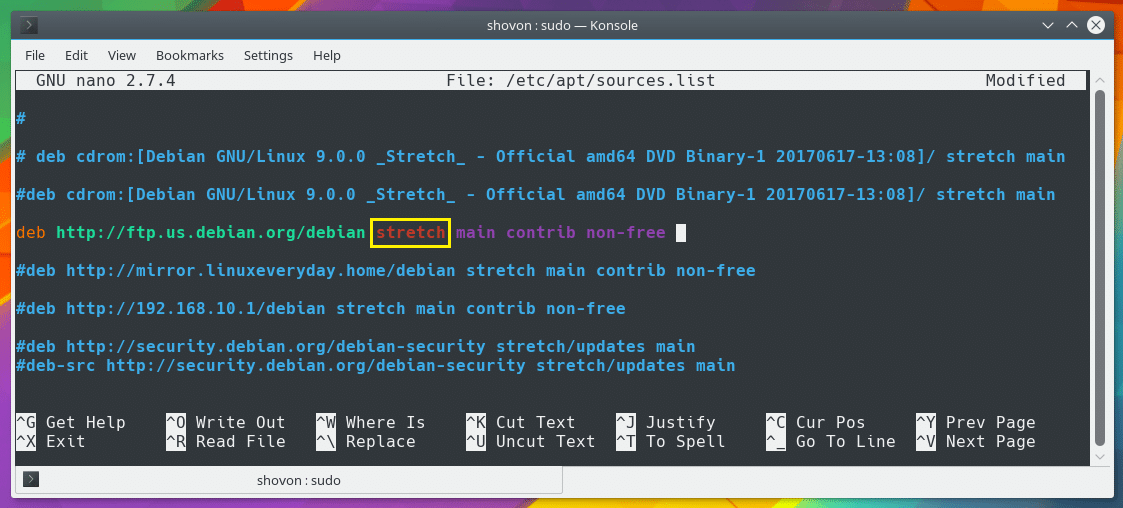
The marked section of the screenshot below depends on the specific package repository that you’re adding. For the official Debian repository, you have main, contrib, and non-free.
Each of these words represents a section or set of software packages on the same package repository.
Once you’re done, press <Ctrl> + x and then press y and then press <Enter> to save the file.
Once you’re done adding a repository, run the following command to update the apt package manager cache:
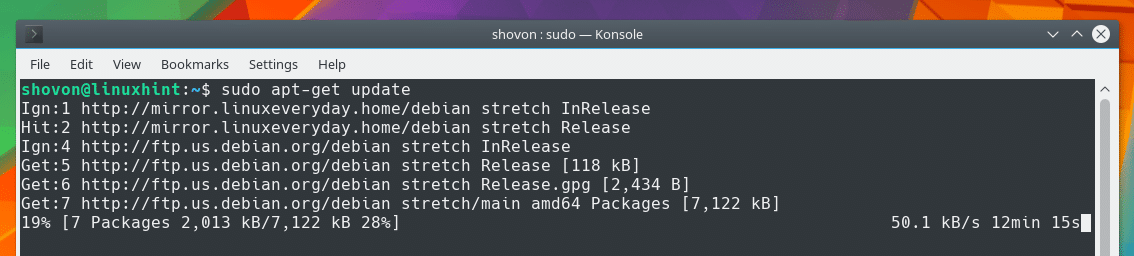
As you can see, the package repository cache is being updated.
There is also a cleaner way to add new package repositories on Debian.
On Debian operating systems, a special directory /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ is available by default. It is used to make adding new package repositories easier. All you have to do is create a new file with the extension .list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory.
Instead of adding the new repository to the /etc/apt/sources.list file, you can create a new file let’s say debian_us_official.list in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory with the following command:

A new empty file should be opened.
Now add the following line to it.
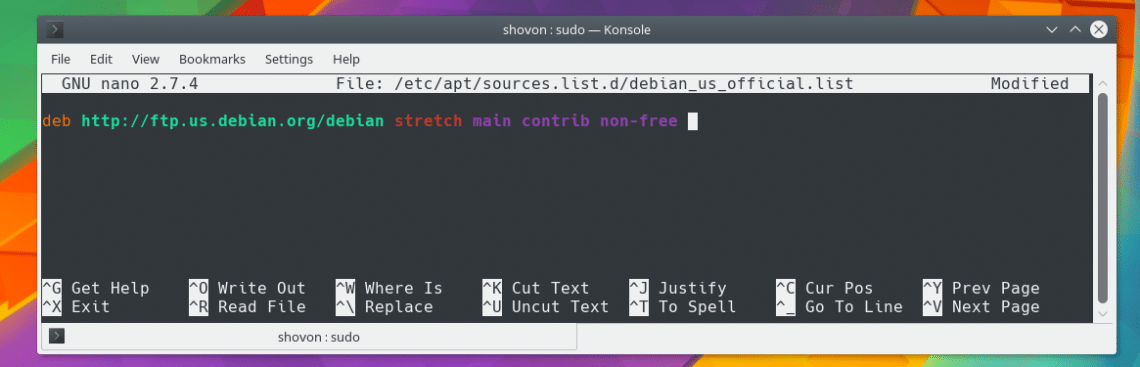
Now save the file and run the following command. You’re good to go.
Adding a Package Repository Using apt on Debian
Now that you understand how a repository line is formatted. You can now use the apt package manager to add new package repositories.
To add the same repository as before, run the following command:

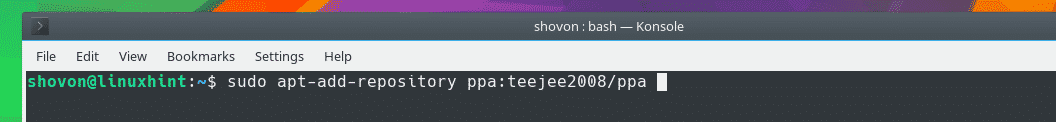
You can add a PPA as well with the following command:
NOTE: Here YOUR_PPA should be something like ppa:teejee2008/ppa.
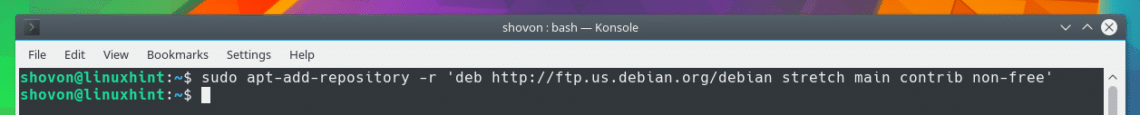
You can also remove a PPA or a package repository with the following command:
NOTE: Here, YOUR_REPOSITORY may be a repository line or a PPA.
For example, in the screenshot below, I removed a repository using the repository line.
That’s how you add a repository on Debian. Thanks for reading this article.






