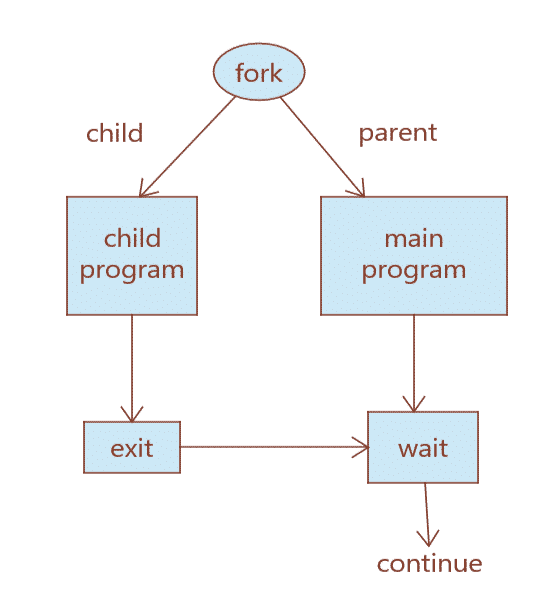
Fig 1: Basic fork() workflow
In this article, I am going to show you how to use fork() system call to create child processes in C. So, let’s get started.
fork() Syntax and Return Value:
The syntax of the fork() system function is as follows:
The fork() system function does not accept any argument. It returns an integer of the type pid_t.
On success, fork() returns the PID of the child process which is greater than 0. Inside the child process, the return value is 0. If fork() fails, then it returns -1.
Simple fork() Example:
A simple fork() example is given below:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
printf("Child => PPID: %d PID: %dn", getppid(), getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else if(pid > 0) {
printf("Parent => PID: %dn", getpid());
printf("Waiting for child process to finish.n");
wait(NULL);
printf("Child process finished.n");
}
else {
printf("Unable to create child process.n");
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
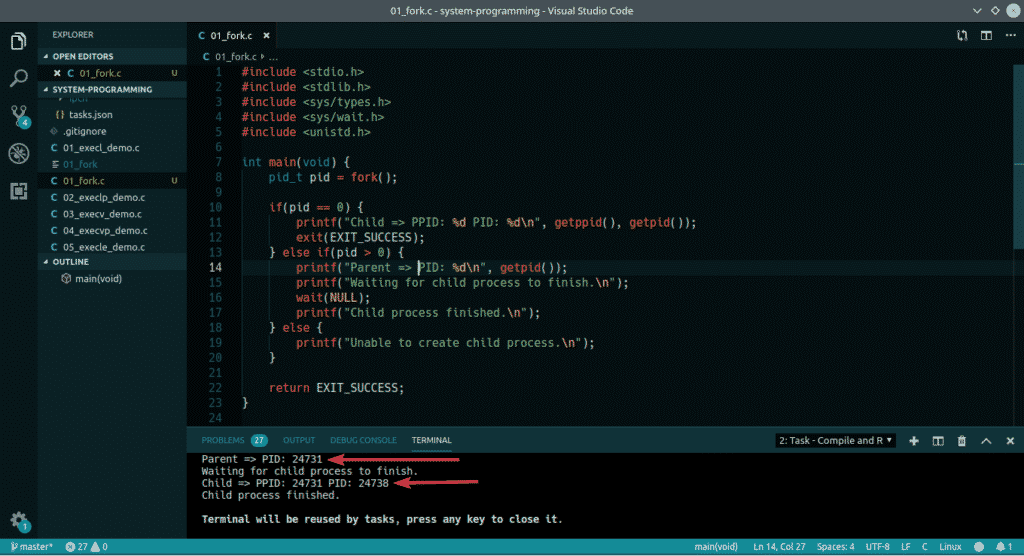
Here, I used fork() to create a child process from the main/parent process. Then, I printed the PID (Process ID) and PPID (Parent Process ID) from child and parent process. On the parent process wait(NULL) is used to wait for the child process to finish. On the child process, exit() is used to finish the child process. As you can see, the PID of the parent process is the PPID of the child process. So, the child process 24738 belongs to the parent process 24731.
You can also use functions to make your program more modular. Here, I used processTask() and parentTask() functions for the child and parent processes respectively. This is how fork() is actually used.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void childTask() {
printf("Hello Worldn");
}
void parentTask() {
printf("Main task.n");
}
int main(void) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
childTask();
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else if(pid > 0) {
wait(NULL);
parentTask();
}
else {
printf("Unable to create child process.");
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
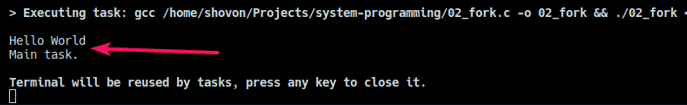
The output of the above program:
Running Multiple Child Processes using fork() and Loop:
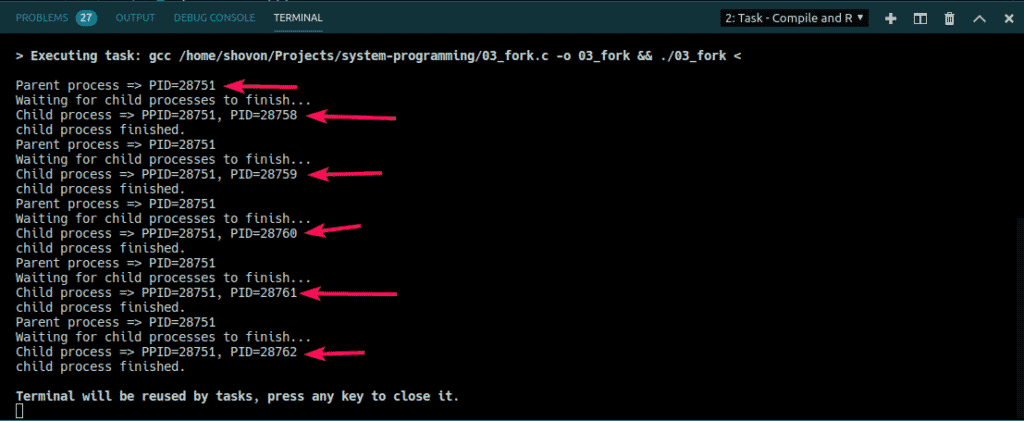
You can also use loop to create as many child processes as you need. In the example below, I have created 5 child processes using for loop. I also printed the PID and PPID from the child processes.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
printf("Child process => PPID=%d, PID=%dn", getppid(), getpid());
exit(0);
}
else {
printf("Parent process => PID=%dn", getpid());
printf("Waiting for child processes to finish…n");
wait(NULL);
printf("child process finished.n");
}
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
As you can see, the Parent process ID is the same in all the child processes. So, all of them belong to the same parent. They also execute in linear fashion. One after the other. Controlling child processes is a sophisticated task. If you learn more about Linux system programming and how it works, you will be able to control the flow of these processes anyway you like.
Real Life Example:
Different complex mathematical computations such as md5, sha256 etc hash generation requires a lot of processing power. Instead of computing things like that in the same process as the main program, you can just calculate the hash on a child process and return the hash to the main process.
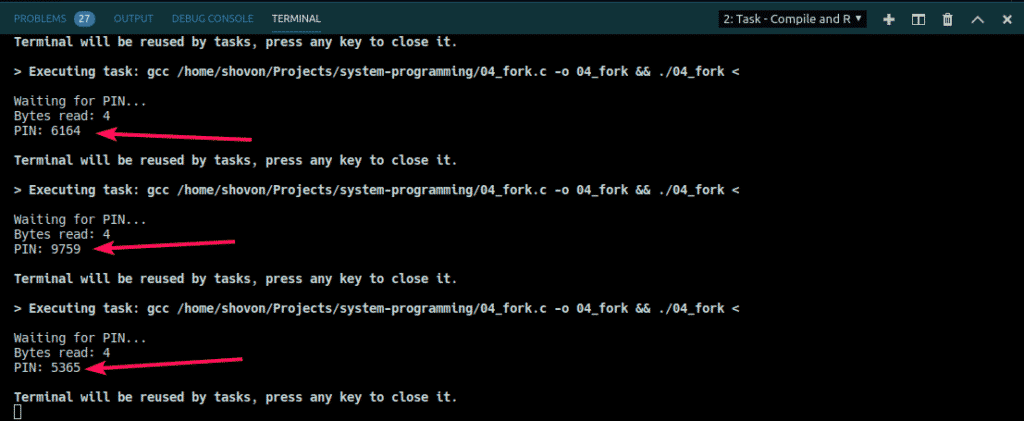
In the following example, I’ve generated a 4-digit PIN code in a child process and send it to the parent process, the main program. Then, I printed the PIN code from there.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int getPIN() {
// use PPID and PID as the seed
srand(getpid() + getppid());
int secret = 1000 + rand() % 9000;
return secret;
}
int main(void) {
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid > 0) {
close(0);
close(fd[1]);
dup(fd[0]);
int secretNumber;
size_t readBytes = read(fd[0], &secretNumber, sizeof(secretNumber));
printf("Waiting for PIN…n");
wait(NULL);
printf("Bytes read: %ldn", readBytes);
printf("PIN: %dn", secretNumber);
}
else if(pid == 0) {
close(1);
close(fd[0]);
dup(fd[1]);
int secret = getPIN();
write(fd[1], &secret, sizeof(secret));
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
As you can see, each time I run the program, I get a different 4-digit PIN code.
So, that’s basically how you use fork() system call in Linux. Thanks for reading this article.