What is Memcached
According to the official Memcached website:
Memcached is an in-memory key-value store for small chunks of arbitrary data (strings, objects) from results of database calls, API calls, or page rendering. Memcached is simple yet powerful. Its simple design promotes quick deployment, ease of development, and solves many problems facing large data caches. Its API is available for most popular languages.
Getting Started
We can get started with Memcached with just a few set of commands. Once the installation has completed, we will also test to verify it has been installed correctly and is running.
Installation
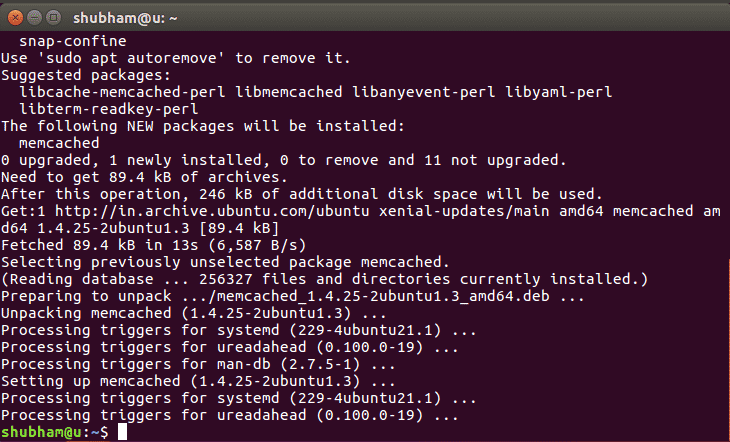
We will run the following apt-get based command to install Memcached on our Ubuntu 16.04 machine:
Here is what we get back with this command:
Starting Memcached
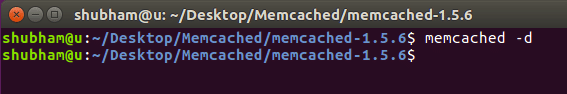
It is easy to start Memcached as a daemon server. By default, Memcached runs on port 11211. We can start using the command:
We can even run multiple instances of Memcached or run it on a different port using the same command:
These two commands produce no output:
Storing Data in Memcached
Now that our Memcached instance has started on port 11211, we can first verify that it is running:

Now, we’re ready to store and get data from memcached. Use the following format while storing data into Memcached:
To get a key, use this format:
To replace key-value, use trhe replace command as:
Finally, to remove key from Memcached, use the delete command:
Let’s try an example:

Conclusion
In this lesson, we looked at how we can install and start using Memcached which is an excellent Object caching system which stores data in the memory itself so that subsequent calls can be made faster to the database.