Coroutine: The part of code that can be paused and resumed in multi-threaded script is called coroutine. coroutines work cooperatively in multi-threaded program. When one coroutine pauses then other coroutine can execute.
Event loop: It is used to start the execution of coroutines and handle input/output operations. It takes multiple tasks and complete them.
Task: The execution and the result of coroutines are defined by the tasks. You can assign multiple number of tasks using asyncio library and run the tasks asynchronously.
Future: It acts as a future storage where the result of coroutines will store after completion. This is useful when any coroutine requires to wait for the result of other coroutine.
How you can implement the above concepts of asyncio library is shown in this tutorial by using some simple examples.
Example-1: Create Single coroutine with a single task
Create a file named async1.py and add the following code. asyncio library is imported to use the functions of this library. add function is declared to calculate the sum of a particular range of numbers. The number range from 1 to 101 is assigned by the task with one second delay. The event loop is declared that it will run until all the tasks of main method complete. After calculating the value, the function will wait for one second and print the result.
async def add(start,end,wait):
#Initialize sum variable
sum = 0
#Calculate the sum of all numbers
for n in range(start,end):
sum += n
#Wait for assigned seconds
await asyncio.sleep(wait)
#Print the result
print(f‘Sum from {start} to {end} is {sum}’)
async def main():
#Assign a single task
task=loop.create_task(add(1,101,1))
#Run the task asynchronously
await asyncio.wait([task])
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
#Declare event loop
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
#Run the code until completing all task
loop.run_until_complete(main())
#Close the loop
loop.close()
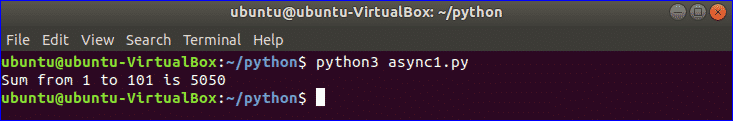
Output:
The output shows the sum of 1 to 101 which is 5050.
Example-2: Create Multiple coroutines
The use of asyncio library will be cleared when you will run multiple coroutines concurrently. Create a new file named async2.py and add the following code. Three tasks are generated with three different ranges and waiting values in main() method. First task will calculate the sum from 5 to 500000 by waiting 3 seconds, second task will calculate the sum from 2 to 300000 by waiting 2 seconds and third task will calculate the sum from 10 to 1000 by waiting 1 seconds. The task with low waiting values will complete at first and the task with high waiting value will complete at last.
async def add(start,end,wait):
#Initialize sum variable
sum = 0
#Calculate the sum of all numbers
for n in range(start,end):
sum += n
#Wait for assigned seconds
await asyncio.sleep(wait)
#Print the result
print(f‘Sum from {start} to {end} is {sum}’)
async def main():
#Assign first task
task1=loop.create_task(add(5,500000,3))
#Assign second task
task2=loop.create_task(add(2,300000,2))
#Assign third task
task3=loop.create_task(add(10,1000,1))
#Run the tasks asynchronously
await asyncio.wait([task1,task2,task3])
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
#Declare event loop
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
#Run the code until completing all task
loop.run_until_complete(main())
#Close the loop
loop.close()
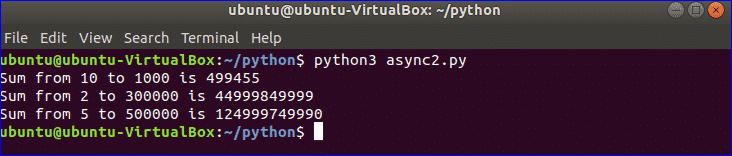
Output:
The output shows that task3 is completed first because the waiting time of this task was only 1 second and task1 is completed last because the waiting time of this task was 3 seconds.
Example-3: coroutines with future
This example shows the use of future object of asyncio library. Create a new file named async3.py and add the following code. Two tasks are assigned for future in this example. show_message function is declared here to print the message before executing the coroutine and after completing the execution. First task will wait for 2 seconds and complete last. Second task will wait for 1 seconds and complete first.
async def show_message(number,wait):
#Print the message
print(f‘Task {number} is running’)
#Wait for assigned seconds
await asyncio.sleep(wait)
print(f‘Task {number} is completed’)
async def stop_after(when):
await asyncio.sleep(when)
loop.stop()
async def main():
#Assign first task
task1=asyncio.ensure_future(show_message(1,2))
print(‘Schedule 1’)
#Assign second task
task2=asyncio.ensure_future(show_message(2,1))
print(‘Schedule 2’)
#Run the tasks asynchronously
await asyncio.wait([task1,task2])
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
#Declare event loop
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
#Run the code of main method until completing all task
loop.run_until_complete(main())
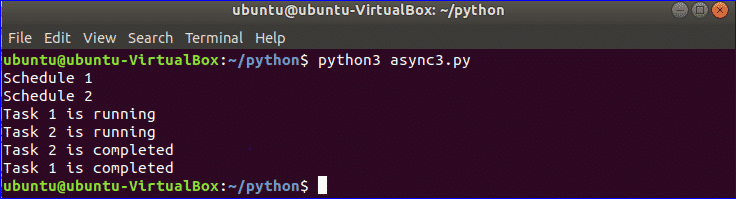
Output:
It is shown in the output that the task1 is started first and completed last, and task2 is started later but completed first for short waiting time.
Conclusion
The basic concept of asynchronous programming using asyncio library of python is explained here. Hope, you will be able to write multi-threaded code in python after practicing the examples of this tutorial.







